Hi Everyone!! This article will share Pronouns and Their Types with examples.
In my previous posts, I have shared Parts Of Speech and Nouns and Its Types so, make sure to check these posts as well.
Pronouns and Their Types With Examples
What Are Pronouns?
- Pronouns are the words used in place of nouns or noun-equivalent.
- Their use help us to avoid repetition of nouns and make sentences shorter.
- Without their use, the language would be lengthy, repetitious and awkward.
For example –
Read the following sentences:
Prapti is fourteen years old. Prapti studies in XYZ International School. Kajal is a classmate of Prapti. Prapti and Kajal walk together to school.
Now, read these:
Prapti is fourteen years old. She studies in XYZ International School. Kajal is a classmate of hers. They walk together to school.
In the second paragraph, you can see that the pronouns have taken the place of some nouns and so, the sentences read more naturally.
*The noun for which a pronoun stands is called its antecedent.
| Antecedent | Pronoun |
| Prapti | She |
| Prapti’s | hers |
| Prapti and Kajal | They |
Pronouns and Their Types With Examples
Types of Pronouns
There are nine types of pronouns:
- Personal Pronouns
- Demonstrative Pronouns
- Interrogative Pronouns
- Possessive Pronouns
- Reflexive Pronouns
- Emphatic Pronouns
- Relative Pronouns
- Indefinite Pronouns
- Reciprocal Pronouns
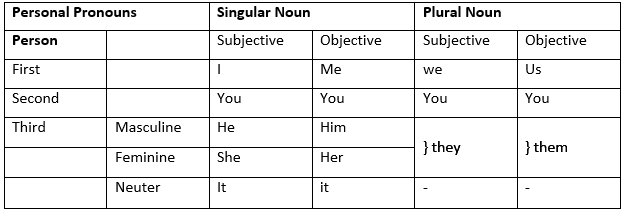
1. Personal Pronoun
- It stands for a specific person/name, object or thing.
- It changes its form to indicate gender (she/he) and number (they/it),
- It may be – first person (I, we), second person (you), third person (she, he, it, they).
- These are of two types:
(a) Subjective – as subject of a sentence
e.g. – She is dancing.
(b) Objective – as object of a verb or preposition
e.g. – Neha is calling you.
2. Demonstrative Pronoun
It is used to point out the object/objects to which they refer.
They are ‘this’, ‘that’ (Singular) and ‘these’, ‘those’ (Plural).
| Object | Singular | Plural |
| nearby | This is a good book. | These are new chairs. |
| far away | That was my old car. | Those are my bags. |
3. Interrogative Pronoun
Usually used at the beginning of the sentence, Interrogative pronoun is used to ask a question.
For example –
(a) ‘Whom’, ‘who’, ‘whose’ is used for people.
- Whom are you complaining about?
- Who helped you?
- Whose pen is this?
(b) ‘Which’ is used for people and things.
- Which is your car?
- Which is the train to Mumbai?
(c) ‘What’ is used for things.
- What are you going to sell?
- What did you eat for lunch?
Pronouns and Their Types
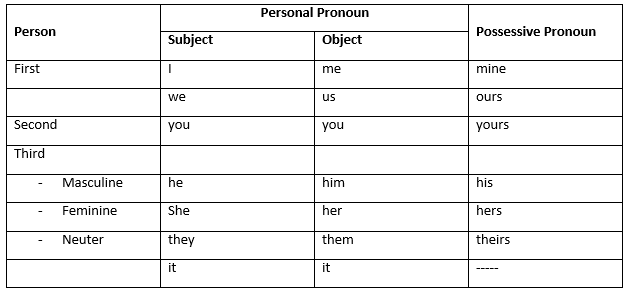
4. Possessive Pronoun
- It shows belongingness or possession and indicates that something belongs to someone.
- Replaces the noun and the possessive adjective.
| Possessive Pronoun | Possessive Adjecive |
| The white car is mine. | The white car is my car. |
| The house is ours. | It is our house. |
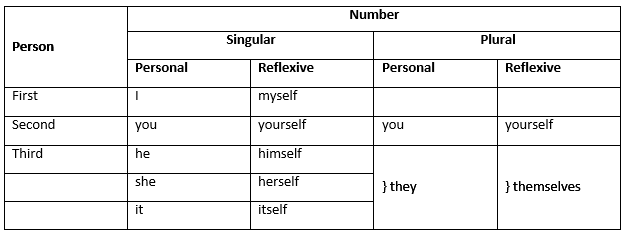
5. Reflexive Pronouns
- It is formed by adding the suffix ‘-self’ (singular) or ‘-selves’ (plural) to simple pronouns like ‘her, me, him, your, them, it and our’.
- So, reflexive pronoun is a ‘self’ form of personal pronoun.
- These can’t be used as the subject of a sentence.
For example –
- I taught myself to read and write.
- The boy fell and hurt himself.
When the subject and the object of the verb refer to the same person, a reflexive pronoun is used for the object. Here, the action of the subject goes back to the doer.
For example –
- Nikhil blamed himself for not locking the main door.
6. Emphatic Pronouns
- When a reflexive pronoun is used to add emphasis on a particular noun or pronoun, it is called an emphatic pronoun.
- It can be removed from the sentence without affecting the ore meaning.
For example –
- They themselves made this rangoli.
- She herself prepared the dinner.
Pronouns and Their Types
7. Relative Pronouns
- These link a phrase or clause in a sentence.
- It relates to the nouns that come before them.
- The words which, who, what, that, whom are relative pronouns.
- Compound words such as whomsoever, whoever, whatever and whichever are also relative pronouns.
- The relative pronoun ‘who’ is not used for things. It is used for a person/people.
For example –
- I know the man who made this sofa.
- Please check whatever he has written.
Position Of Relative Pronoun
- They are usually used in the middle of the sentence. Please refer to the above examples.
- However, the relative pronouns such as ‘whom’, ‘who’ and ‘what’ can be used in the beginning of the sentence when the antecedent is understood.
For example –
What has happened is not at all clear. (I don’t know what has happened)
- This pronoun must be of the same number and person as its antecedent.
For example –
- The woman who was brave was rewarded.
- The women who were brave were rewarded.
8. Indefinite Pronouns
- It refers to things or people in a general way but doesn’t exactly say who or what they are.
- Pronouns ending in –thing are used for things. And the words ending in –body are used for people. For example – nobody, something, everybody, etc.
- The words such as each, some, few, one, others, one’s, none, etc. are indefinite pronouns.
For example –
- Do you want this pen or the other?
- Everybody was silent.
These pronouns agree with the singular form of verb.
For example –
- Everyone was ready for the ceremony.
9. Reciprocal Pronouns
These are words that convey a sense of reciprocation which means a mutual exchange of ideas and emotions.
For example –
- The two artists complimented each other on their performances.
So, this was all about Pronouns and Their Types.